- #1
sss1
- 50
- 2
- Homework Statement
- Is my understanding of nuclear fusion and binding energy correct?
- Relevant Equations
- NA
Binding energy- the amount of energy required to dissemble the nucleus
High binding energy means that the nucleus is very tightly bound, whereas a low binding energy means the nucleus is weakly bound.
The nuclear strong force acts at a very short range whereas the Coulomb force is infinite range.
For small nuclei, adding extra nucleons means there are more nucleons the nuclear strong force to act on, and the coulomb repulsion force is not so strong yet, so the binding energy increases.
When a proton gets added into a nucleus, it will feel Coulomb repulsion from ALL the other protons but only feel the nuclear strong force from its close neighbors. Hence for heavy nuclei, the binding energy decreases after iron because the Coulomb force starts to dominate instead of the strong force? When you fuse, you go from being unstable to being stable (before iron), unstable having lower binding energy and stable having higher binding energy.
For the unstable ones, having lower binding energy, I’d be imagining nucleons vibrating all over the place? So they have excess energy. When they fuse or fission to become more stable, do the nucleons lose energy because the new nuclei vibrate less? That energy is equal to the difference in the binding energies?
If so, for this question, bii, would 28-2-3(2.7) be a good approximation?
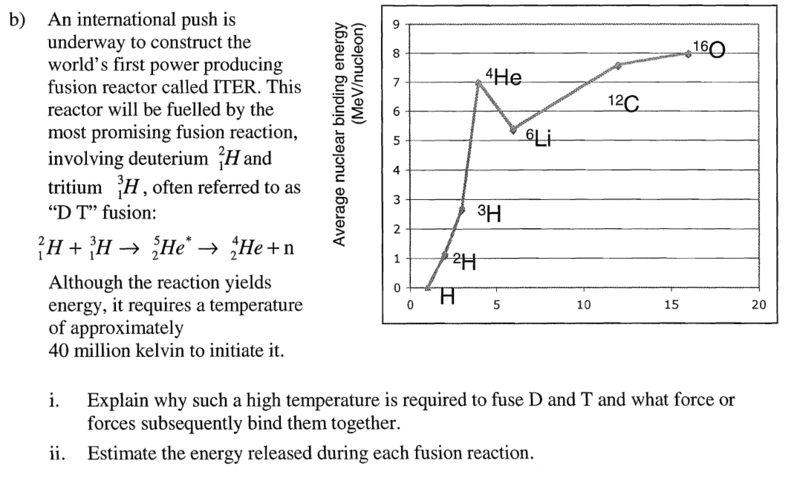
If so, for this question, bii, would 28-2-3(2.7)=17.9MeV be a good approximation?
High binding energy means that the nucleus is very tightly bound, whereas a low binding energy means the nucleus is weakly bound.
The nuclear strong force acts at a very short range whereas the Coulomb force is infinite range.
For small nuclei, adding extra nucleons means there are more nucleons the nuclear strong force to act on, and the coulomb repulsion force is not so strong yet, so the binding energy increases.
When a proton gets added into a nucleus, it will feel Coulomb repulsion from ALL the other protons but only feel the nuclear strong force from its close neighbors. Hence for heavy nuclei, the binding energy decreases after iron because the Coulomb force starts to dominate instead of the strong force? When you fuse, you go from being unstable to being stable (before iron), unstable having lower binding energy and stable having higher binding energy.
For the unstable ones, having lower binding energy, I’d be imagining nucleons vibrating all over the place? So they have excess energy. When they fuse or fission to become more stable, do the nucleons lose energy because the new nuclei vibrate less? That energy is equal to the difference in the binding energies?
If so, for this question, bii, would 28-2-3(2.7) be a good approximation?
If so, for this question, bii, would 28-2-3(2.7)=17.9MeV be a good approximation?
Last edited by a moderator: