- #1
Mr Joe Bangles
- 3
- 0
Hello, quick question here
I am studying mathematical astronomy / the history of , and I have noted that by raising the average sidereal period of any planet in our solar system, to the power .666666, that you are left with the average distance of that planet from the Sun, in AU
I was told that this is essentially Kepler's 3rd law, restated, and that it was a " geometric relationship "
However, I am not a mathematician and don't understand how this

translates to this
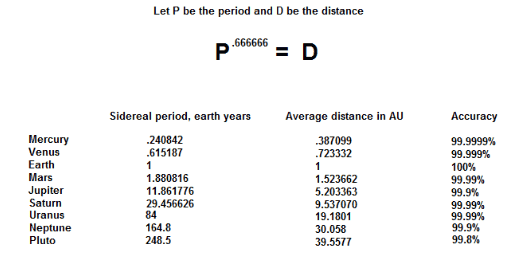 Can somebody help clear this up for me ?
Can somebody help clear this up for me ?
Thanks,
Joe
I am studying mathematical astronomy / the history of , and I have noted that by raising the average sidereal period of any planet in our solar system, to the power .666666, that you are left with the average distance of that planet from the Sun, in AU
I was told that this is essentially Kepler's 3rd law, restated, and that it was a " geometric relationship "
However, I am not a mathematician and don't understand how this
translates to this
Thanks,
Joe