- #1
KT KIM
- 24
- 0
In basic level classical mechanics I've known so far
The Lagrangian Equation is
Like this
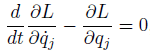
But in the little deeper references, they covers Lagrangian Equation is
Like this
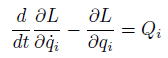
Qi is Generalized force, and Qi also contains frictions that's what reference says
But I still can't grasp.
What is the difference between these two equation, and What Is "Generalized Force" ?
The Lagrangian Equation is
Like this
But in the little deeper references, they covers Lagrangian Equation is
Like this
Qi is Generalized force, and Qi also contains frictions that's what reference says
But I still can't grasp.
What is the difference between these two equation, and What Is "Generalized Force" ?