- #1
MP97
- 4
- 0
Hi, I have been working on deriving the second Newton's law from the Mapertius principle applied to a perfectly elastic collision from a free fall acceleration problem. These are my calculations, but I keep getting a coefficient of 2 in my final answer for some reason. Could someone explain to me what I am doing wrong?
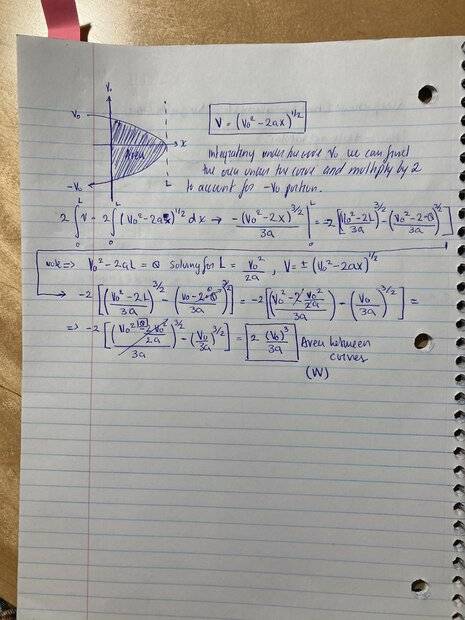

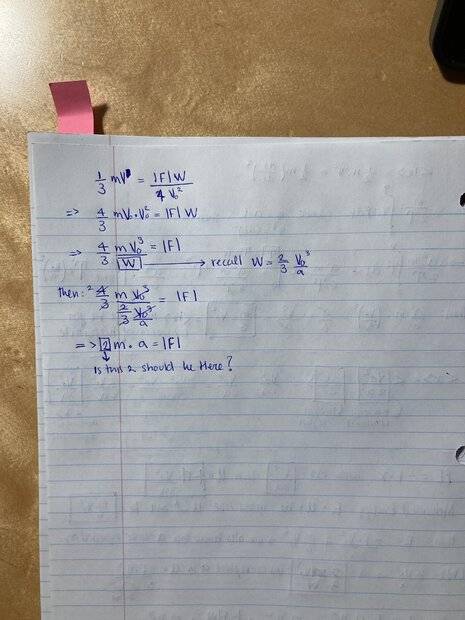
I appreciate any help you can provide!
I appreciate any help you can provide!