- #1
WMDhamnekar
MHB
- 376
- 28
Hi,
I didn't understand the maths involved in the below article in regard to temperature and ideal gas thermometer. If any member knows it, may reply me.

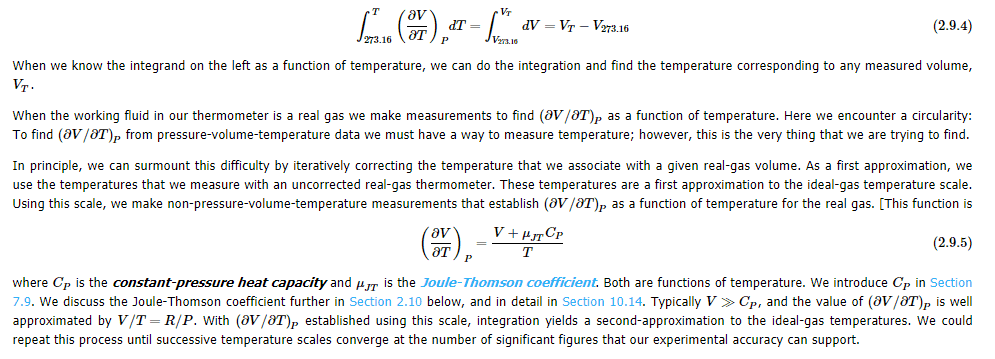
If triple point of water is fixed at 273.16 K, and experiments show that freezing point of air-saturated water is 273.15 K at 1 atm system pressure.(so, melting point of ice is also 273.15 K , then how triple point of water is $0.10^\circ C$ What is meant by real gas volume at thermal equilibrium with a system whose true temperature is $V_T$ be V. In this Math symbol$\big(\frac{\partial V}{\partial T}\big)_P$ what does subscript P indicate? My guess P means Partial.
I am stuck here. If get the answers to my questions satisfactorily, i shall proceed further.
I didn't understand the maths involved in the below article in regard to temperature and ideal gas thermometer. If any member knows it, may reply me.
If triple point of water is fixed at 273.16 K, and experiments show that freezing point of air-saturated water is 273.15 K at 1 atm system pressure.(so, melting point of ice is also 273.15 K , then how triple point of water is $0.10^\circ C$ What is meant by real gas volume at thermal equilibrium with a system whose true temperature is $V_T$ be V. In this Math symbol$\big(\frac{\partial V}{\partial T}\big)_P$ what does subscript P indicate? My guess P means Partial.
I am stuck here. If get the answers to my questions satisfactorily, i shall proceed further.