- #1
baby_1
- 159
- 15
Homework Statement
I obtain Autocorrelation function of two signal:
as
Homework Equations
[/B]
The Attempt at a Solution
[/B]
I want to know what is Normalized Autocorrelation of above equation?
Thanks
What have you tried so far?baby_1 said:Homework Statement
I obtain Autocorrelation function of two signal:
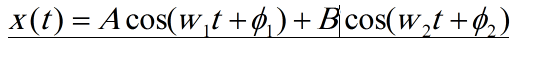
as
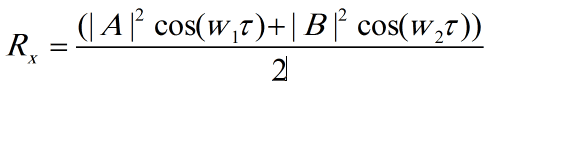
Homework Equations
[/B]The Attempt at a Solution
[/B]
I want to know what is Normalized Autocorrelation of above equation?
Thanks
Sorry if this is a dumb question, but how can you form an autocorrelation between different functions? Can you show your detailed work?baby_1 said:Thanks for your response
I don't know I did right or it should be something else
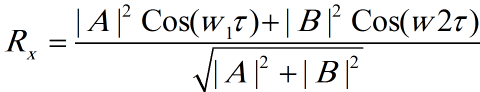
or
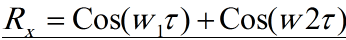
or
...?
Normalized autocorrelation is a statistical method used to measure the similarity between two signals. It calculates the correlation coefficient between the two signals, which represents the strength and direction of their relationship.
The formula for normalized autocorrelation involves taking the covariance of the two signals and dividing it by the product of their standard deviations. This results in a value between -1 and 1, with higher values indicating a stronger correlation.
Normalized autocorrelation is commonly used in signal processing and time series analysis to determine if there is a repeating pattern or relationship between two signals. It can also be used to identify the time delay between two signals.
The main difference is that normalized autocorrelation takes into account the scale and magnitude of the signals, while standard autocorrelation does not. This makes normalized autocorrelation more useful for comparing signals with different scales.
Normalized autocorrelation assumes that the signals are stationary and have a linear relationship. It may also give misleading results if the signals have a high level of noise. Additionally, it may not capture more complex relationships between signals, such as non-linear or time-varying relationships.