- #1
spectastic
- 38
- 1
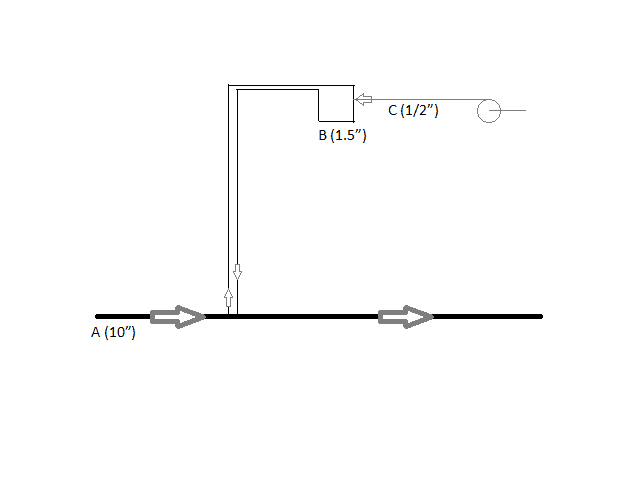
see attached. the main 10" header is water, and the 1/2" chemical injection is polymer feed (not sure how much by volume, we go by pump strokes). problem is during winter, the polymer becomes viscous, and the pump has a hard time pumping the stuff all the way to the header. So we're thinking about putting in a small header that mixes the polymer feed. this 1 1/2" line would run off the supply header pressure from the 10" header. However, because the two 1 1/2" nozzles are so close to each other (like 1 ft), I'm worried that I won't get any flow through the 1 1/2" pipe. I don't want to have to put in a pump if I don't have to.