- #1
Figaro
- 103
- 7
I want to plot a function f(x) such that it's domain is from 1 to 10000 but I want the graph to read 1, 10, 100, 1000, 10000 in the x-axis, while the y-axis is normal.
##f(x) = 2\sin^{-1} ( e^{-\frac{60}{x}})##
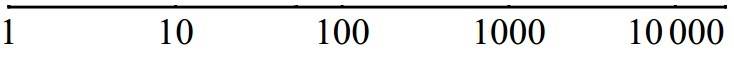
##f(x) = 2\sin^{-1} ( e^{-\frac{60}{x}})##