- #1
tzx9633
Homework Statement
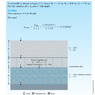
Why there's no pore pressure due to capillary rise at point A and point D ? There's only pore pressure due to capillary rise at B ..
Homework Equations
The Attempt at a Solution
i think the author is wrong . There's should be also ore pressure due to capillary rise at A and D . Because the capillary rise can occur anywhere in the soil .