- #1
Adel Makram
- 635
- 15
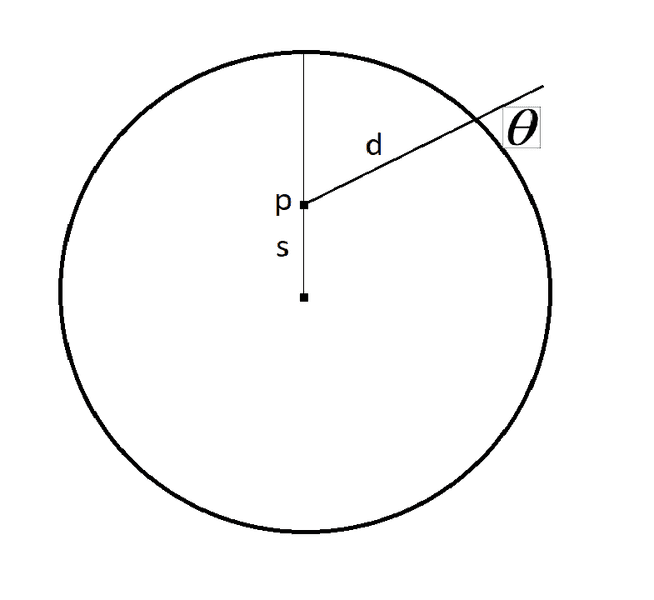
I wish to find a closed form relation between ##\theta## and ##d## in the attached figure as a function of ##r##, the radius of the circle and ##s## the distance from the point ##p## to the center.
Thank you.
Thank you.