- #1
- 2,486
- 9,720
Complex biological entities (like cells) can replicate while things (like molecules or organelles) can replicate within their internal environment.
Here is a nice schematic picture of what is going on in these situations:
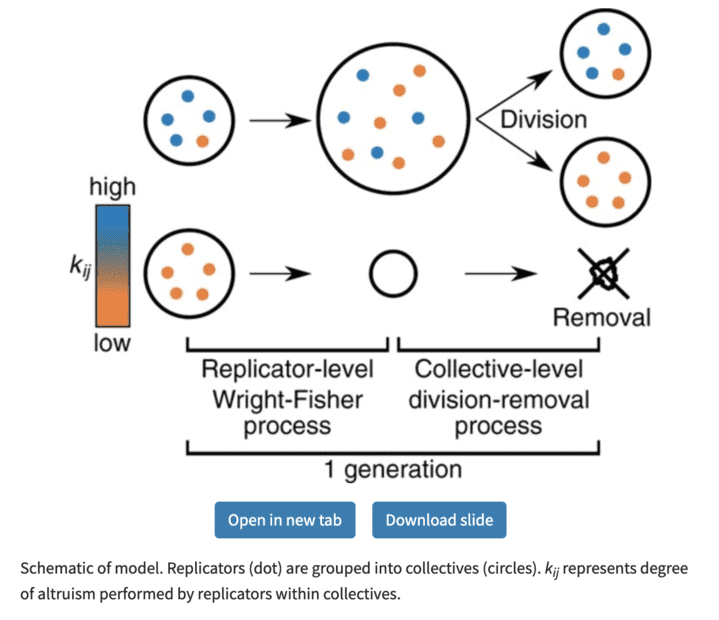
From the article:
Nobuto Takeuchi, Namiko Mitarai, Kunihiko Kaneko, A scaling law of multilevel evolution: how the balance between within- and among-collective evolution is determined, Genetics, Volume 220, Issue 2, February 2022, iyab182, https://doi.org/10.1093/genetics/iyab182
Here is a nice schematic picture of what is going on in these situations:
From the article:
Nobuto Takeuchi, Namiko Mitarai, Kunihiko Kaneko, A scaling law of multilevel evolution: how the balance between within- and among-collective evolution is determined, Genetics, Volume 220, Issue 2, February 2022, iyab182, https://doi.org/10.1093/genetics/iyab182