- #1
QuantumDuality
- 10
- 0
I know there's a similar post, but i didn't understand it. Why the derivative respect to t in terms of the complex conjugate of ψ is:

instead of being the original S.E in terms of ψ*
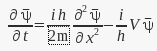
or the equation in terms of ψ with the signs swapped
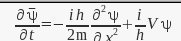
instead of being the original S.E in terms of ψ*
or the equation in terms of ψ with the signs swapped