- #1
panda02
- 2
- 0
- Homework Statement
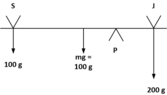
- If Sara (100kg) and Jim (200kg) are 1m from the edge of opposite sides of a 13m long, 100kg see-saw, where does the pivot point need to be in order to balance the see-saw?
- Relevant Equations
- Ts=Tj
Torque_left = 100 kg * 1 m = 100 kg·m
Torque_right = 200 kg * (13 - x) m = 200(13 - x) kg·m
100 kg·m = 200(13 - x) kg·m
100 = 200(13 - x)
x = 12.5 meters
pivot = 12.5 m
Torque_right = 200 kg * (13 - x) m = 200(13 - x) kg·m
100 kg·m = 200(13 - x) kg·m
100 = 200(13 - x)
x = 12.5 meters
pivot = 12.5 m
 ##\qquad## !
##\qquad## !