- #1
Ted goldmund lee
- 3
- 0
- TL;DR Summary
- It feels like the shape of the blasting laser have to be planar because the gain medium itself looks like rectangular.
I read about semiconductor laser and its beam shape is conical with 50' of dispersion angle.
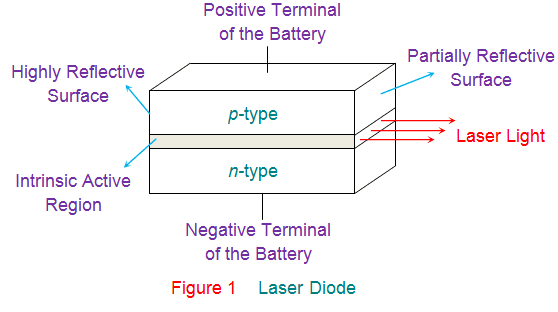
But for me, it is hard to accept that it is conical because every single drawing I see is rectangular and the plan that laser going out is also a plain, not a hole.
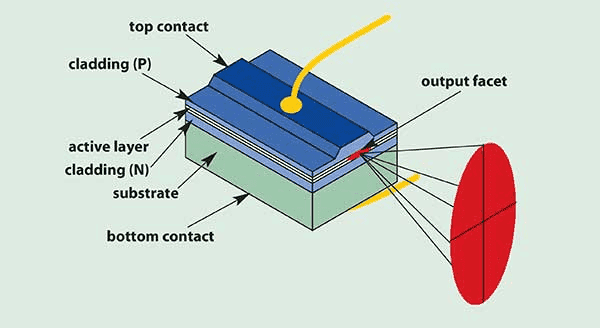
And this is the picture I saw earlier.
Please help me..
But for me, it is hard to accept that it is conical because every single drawing I see is rectangular and the plan that laser going out is also a plain, not a hole.
And this is the picture I saw earlier.
Please help me..