- #1
greswd
- 764
- 20
Let's say you know all 3 cartesian components of a particle's velocity and all 3 for it's acceleration.
You can split the acceleration vector into two vectors, one parallel (longitudinal) to the velocity vector and one perpendicular (transverse) to the velocity vector.
Then, I found the x-components of both acceleration vectors in terms of the 6 variables listed at the start. That would be the component of each acceleration vector parallel to the x-axis. I used the dot product to derive it.
As you can see below, I multiplied the transverse-x acceleration component by gamma and the longitudinal-x acceleration component by gamma cube. These are the formulas for the longitudinal and transverse masses.
I can get a formula for the x-component of the Force.
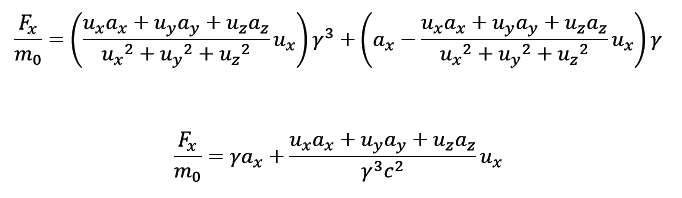 In order to get the second formula, I differentiated the x-component of the 3-momentum with respect to time.
In order to get the second formula, I differentiated the x-component of the 3-momentum with respect to time.
I expected both equations to be equivalent, but try as I might, I can't make them equal.Can you help me spot the error(s) in my formulas?
You can split the acceleration vector into two vectors, one parallel (longitudinal) to the velocity vector and one perpendicular (transverse) to the velocity vector.
Then, I found the x-components of both acceleration vectors in terms of the 6 variables listed at the start. That would be the component of each acceleration vector parallel to the x-axis. I used the dot product to derive it.
As you can see below, I multiplied the transverse-x acceleration component by gamma and the longitudinal-x acceleration component by gamma cube. These are the formulas for the longitudinal and transverse masses.
I can get a formula for the x-component of the Force.
I expected both equations to be equivalent, but try as I might, I can't make them equal.Can you help me spot the error(s) in my formulas?