- #1
SnakeDoc
- 27
- 1
Homework Statement
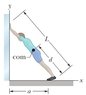
In the figure, a climber leans out against a vertical ice wall that has negligible friction. Distance a is 0.905 m and distance L is 2.15 m. His center of mass is distance d = 0.91 m from the feet-ground contact point. If he is on the verge of sliding, what is the coefficient of static friction between feet and ground?
Homework Equations
x: 0= W-ƒ
y: 0= N+mg
Torque
T=L x F
0= N(A)-(1.95)ƒ-(.52195)mg
ƒ=μN
The Attempt at a Solution
I drew a FBD and came up with
x: 0= W-ƒ
y: 0= N+mg
putting them in a state of equilibrium.
Find than
then I did the torques and
T: 0 = Nτ-ƒτ-mgτ
Unsure how to proceed I used the WileyPlus' go tutorial feature it asked me for what it called the moment arms of the Normal force, Force due to gravity, and frictional force after a few guesses because I was unsure what it was asking for it gave all three values but I would like to know what it was asking for how =to find them. The values were as follows
moment arm for Normal force: .905
moment arm for Force due to Gravity: .52195
moment arm for Frictional Force: 1.95
I understand that they become the L value of each torque but I don't understand how they found each.
T: 0= N(.905)-ƒ(1.95)-mg(.52195) since N=MG and ƒ=mg substitute
T: 0= mg(.905)-μmg(1.95)-mg(.52195)<<mg's cancel
T: 0=(.905)-μ(1.95)-(.5195) <<simplify
T: μ=.196