- #1
DYLAN4321
- 4
- 0
- TL;DR Summary
- Plate with hole help
Hi,
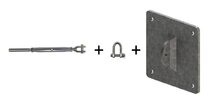
I have developed a catenary software that calculates the tension force resulting from the wire and now I am working on suitable fixing methods and including the option for this within the software.
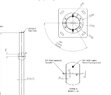
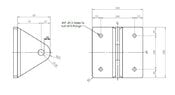
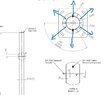
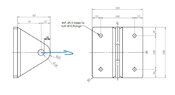
Has anyone got any guidance on working out the stresses applied on the attached applications? Also how woudl the circular plate act if there were multiple wires pulling in different directions?
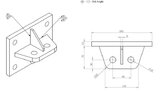
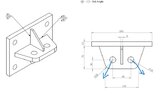
I have done a quick mock up for a plate with multiple holes, but this isn`t really applicable to these applciations given the holes are positioned close to the edge of the plates.
Any help will be appreciated
I have developed a catenary software that calculates the tension force resulting from the wire and now I am working on suitable fixing methods and including the option for this within the software.
Has anyone got any guidance on working out the stresses applied on the attached applications? Also how woudl the circular plate act if there were multiple wires pulling in different directions?
I have done a quick mock up for a plate with multiple holes, but this isn`t really applicable to these applciations given the holes are positioned close to the edge of the plates.
Any help will be appreciated
Attachments
Last edited: