- #1
ffp
- 97
- 5
Thread moved from the technical forums to the schoolwork forums
Ok, now I'm studying symmetrical components. Im using Stevenson's Power System Analysis book and example 11.9 asks for the zero sequence circuit of the example 6.1 in the same book.
Here's the example and the solution:

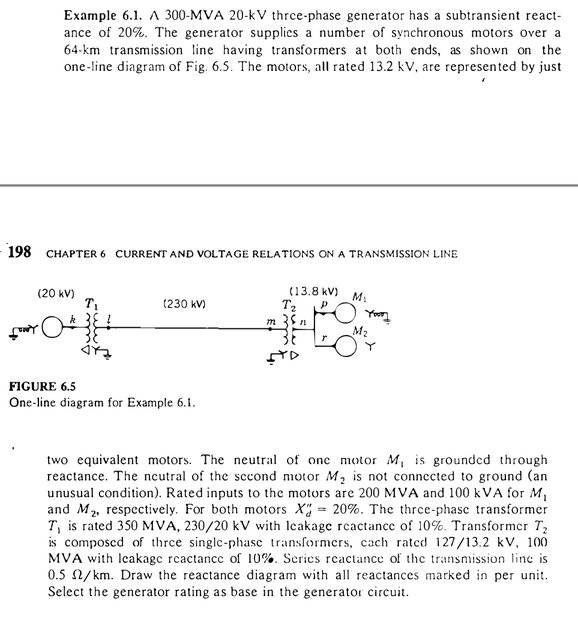
Here's example 6.1, so we can see what is the circuit:
Here's the beggining of the solution, where I'm stuck...

I believe de X of T1 (0.0857 pu) is found by changing bases (Xpu=OLDpu x OLDbase/NEWbase). So 0.1 is the pu of T1, 300 is the Sbase (MVA) of the generator (and hence, system) and 350 is the Sbase (MVA) of T1. Is that right?
If so, why is X of T2 calculated differently, I believe by reflecting impedances? If that's really what he's doing, why is he using 13.2 and 13.8?
I'm really lost here with this example.
Here's the example and the solution:
Here's example 6.1, so we can see what is the circuit:
Here's the beggining of the solution, where I'm stuck...
I believe de X of T1 (0.0857 pu) is found by changing bases (Xpu=OLDpu x OLDbase/NEWbase). So 0.1 is the pu of T1, 300 is the Sbase (MVA) of the generator (and hence, system) and 350 is the Sbase (MVA) of T1. Is that right?
If so, why is X of T2 calculated differently, I believe by reflecting impedances? If that's really what he's doing, why is he using 13.2 and 13.8?
I'm really lost here with this example.

