- #1
paulimerci
- 287
- 47
- Homework Statement
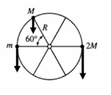
- A wheel of radius R and negligible mass is mounted on a horizontal frictionless axle so that the wheel is in a vertical plane. Three small objects having masses m, M, and 2M, respectively, are mounted on the rim of the wheel, as shown. If the system is in static equilibrium, what is the value of m in terms of M ?
- Relevant Equations
- Rotational equilibrium:
T = F × r × sinθ. T = torque. F = linear force. r = distance measured from the axis of rotation to where the application of linear force takes place.
Applying rotational equilibrium at the center pivot we get:
+mg(R) + Mg(Rcos60°)–2Mg(R) = 0.Using cos60° = ½ we arrive at the answer 3M/2
I don't understand why cosine is used instead of sine in the above equation. I see the y component mg is acting perpendicular to the x component and so from the equation of Torque we understand that the force perpendicular to "r" is taken into consideration. I would really appreciate if anyone could explain.
+mg(R) + Mg(Rcos60°)–2Mg(R) = 0.Using cos60° = ½ we arrive at the answer 3M/2
I don't understand why cosine is used instead of sine in the above equation. I see the y component mg is acting perpendicular to the x component and so from the equation of Torque we understand that the force perpendicular to "r" is taken into consideration. I would really appreciate if anyone could explain.