- #1
samy4408
- 62
- 9
- TL;DR Summary
- I need a satisfactory explanation about alveolar surface tension
Hello, I learned recently about alveolar surface tension, and the explanation provided in the course was not satisfactory, it said that it is due to the force that pushes water molecules of the outer layer to the inner layers, I don't understand why this force that pushes water toward the cell walls is the origin of another force that pusher water in the opposite direction.
can someone give me a satisfactory explanation, tanks.
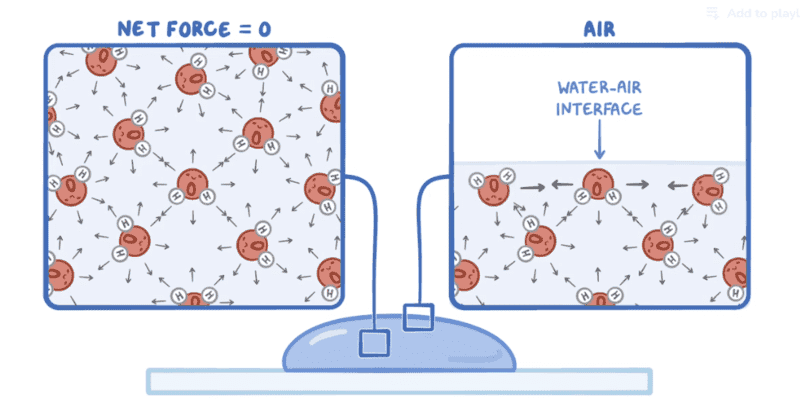
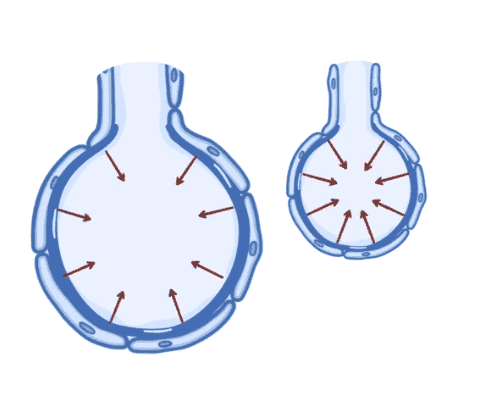
can someone give me a satisfactory explanation, tanks.