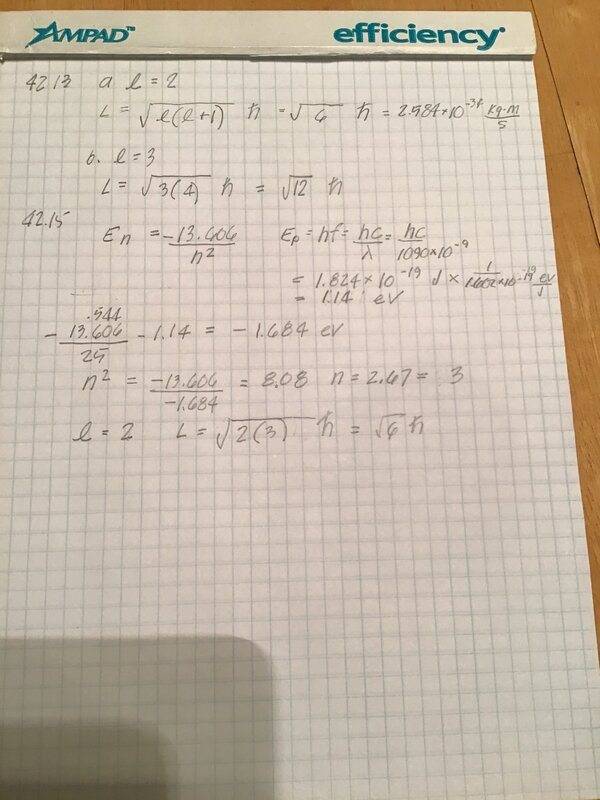- #1
jjson775
- 101
- 23
- Homework Statement
- 42.15 A hydrogen atom is it its 5th excited state. The atom emits a 1 090 nm wavelength photon. Determine the maximum possible orbital angular momentum of the electron after emission.
- Relevant Equations
- En = -13.606/h^2
E = hf
I don’t understand how energy is conserved here. The energy of the atom when n=5 is -.544eV. The energy of the photon is 1.14eV. After release, the energy of the atom is -.544 - 1.14 = 1.68eV. Using this value, I get n = 2.67, not an integer, so n = 3 and the atom has energy = -1.51 eV. I have the right answer but am missing something basic.