- #1
Bolter
- 262
- 31
- Homework Statement
- Work out value of multiplier resistance
- Relevant Equations
- See below
This is the problem itself shown below

And this is what I have tried, I get an answer of 29 ohms
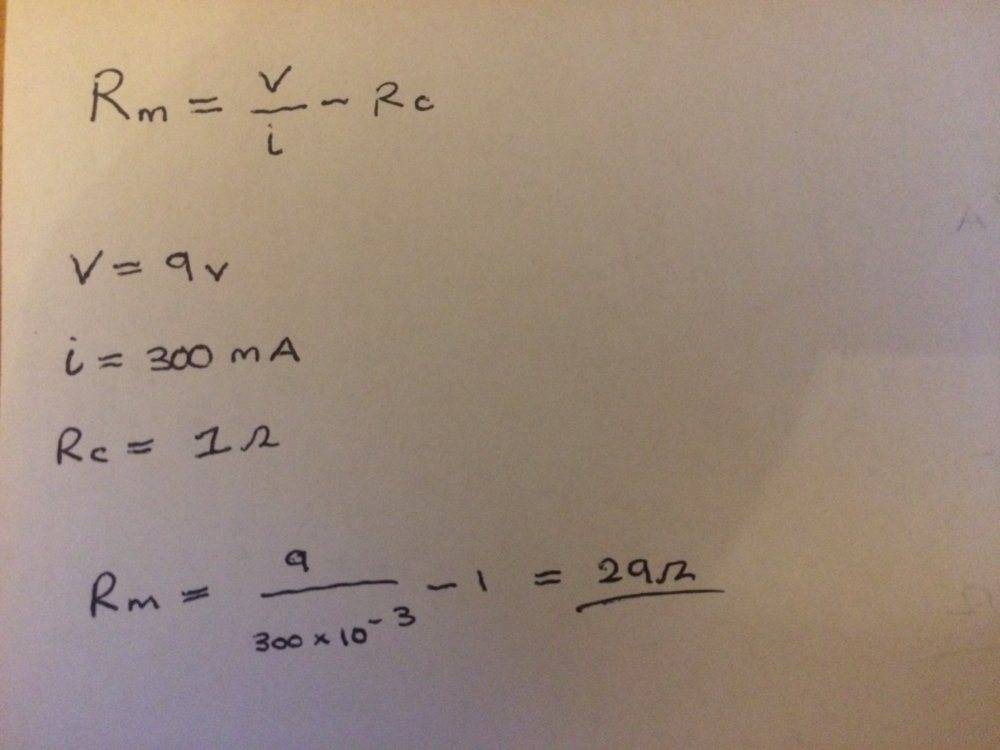
Would you agree?
And this is what I have tried, I get an answer of 29 ohms
Would you agree?