- #1
Vivek98phyboy
- 34
- 5
- Homework Statement
- A uniform rod of length L pivoted at its upper end hangs vertically. It is displaced through an angle of 60° and then released. Find the magnitude of the force acting on a particle of mass 'dm' at the tip of the rod when the rod makes an angle of 37° with the vertical.
- Relevant Equations
- Tangential acceleration of tip(dm), a= L𝛂
After solving using energy conservation, I found the angular velocity at 37° to be omega=2.97/(L)^½
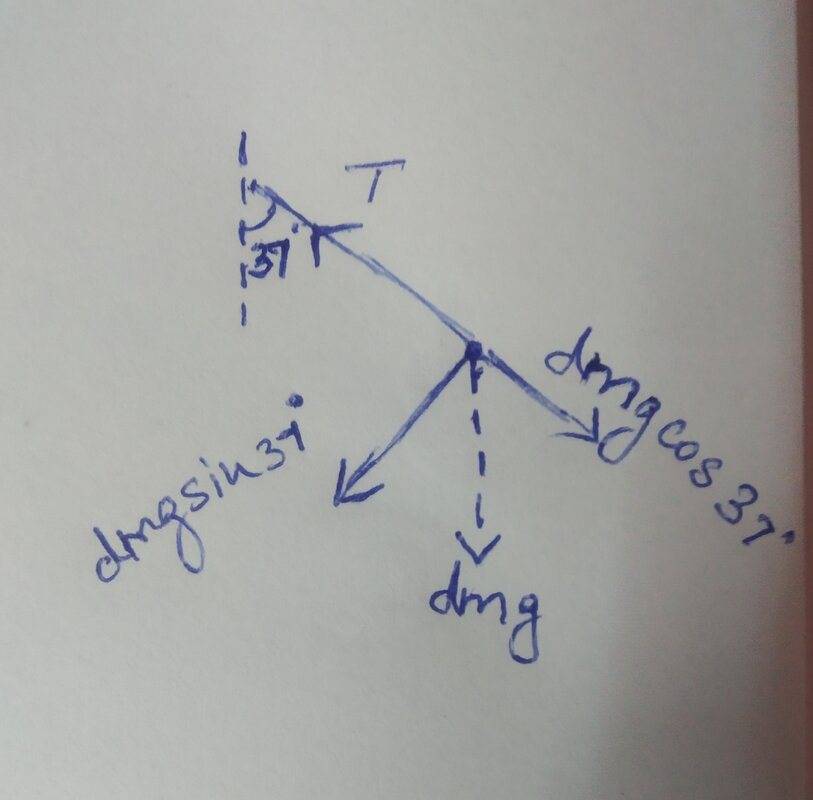
Tension and the weight (dm)g are the two forces acting on the tip dm
To find the resultant force, I resolved the centripetal force and tangential force to find the centripetal force as
F= (dm)(L)(omega)²
and tangential force as (dm)(g)sin37°.
This would leave me with a tangential acceleration of 5.9 m/s²
But when I calculated it using torque, I found the tangential acceleration to be 8.82m/s² and that is the solution given in my book
What am I doing wrong while resolving the forces?
I would also like to know what would be the forces provided by the part of rod that is above 'dm'?
Tension and the weight (dm)g are the two forces acting on the tip dm
To find the resultant force, I resolved the centripetal force and tangential force to find the centripetal force as
F= (dm)(L)(omega)²
and tangential force as (dm)(g)sin37°.
This would leave me with a tangential acceleration of 5.9 m/s²
But when I calculated it using torque, I found the tangential acceleration to be 8.82m/s² and that is the solution given in my book
What am I doing wrong while resolving the forces?
I would also like to know what would be the forces provided by the part of rod that is above 'dm'?