- #1
Adams2020
- 39
- 3
- Homework Statement
- Using the data of Table, what is the recoil energy of a 17O nucleus produced in its first energy level?
- Relevant Equations
- ...
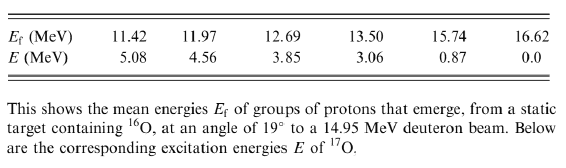
Table:
To solve, using the conservation of energy:
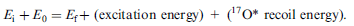
E0=(m(deutron)+m(16O)-m(17O)-m(p))c^2
so:
E0=(2.014+15.994-16.999-1.008)931.5=0.93 MeV.
so using the conservation of energy:
14.95+0.93=16.62+0+E'
E'=- 0.74 MeV
But the energy sign has become negative. I also calculated for the first excited level, it was negative again. I do not know what is wrong.
To solve, using the conservation of energy:
E0=(m(deutron)+m(16O)-m(17O)-m(p))c^2
so:
E0=(2.014+15.994-16.999-1.008)931.5=0.93 MeV.
so using the conservation of energy:
14.95+0.93=16.62+0+E'
E'=- 0.74 MeV
But the energy sign has become negative. I also calculated for the first excited level, it was negative again. I do not know what is wrong.