- #1
Jadejadeface
- 1
- 0
Homework Statement
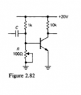
1. Additional Exercise 7 in the textbook (H&H, p. 110). Vout is 0.5Vcc at the quiescent point. You may assume beta = 100. The transistor is said to saturate when VC = VB. Use the fact IC grows 9%/ degree C and that VBE is constant to determine when the transistor saturates.
Homework Equations
Vb = Vbe +IeRe
Vcc = IcRc + Vce + IeRe where Ic = (beta x Ie)/(beta +1)
The Attempt at a Solution
Ok, so firstly I'm confused about whether we need to answer 7 and this question or just what's written in "1.". Anyway, for Vb = 0.5Vcc the two resistors must be equal ( I don't really understand what that arrow is pointing to the resistor, please explain? Since the problem says he adjusts it until 0.5Vcc is reached I'm assuming both resistors = 1K) Therefore Vout = 10V = Vb.
And this is as far as I get since there is no Re I'm not really sure about how to get Vc. If there was a resistor there I would find Vc using the above equation then figure how much I need to increase the temperature to get Vc = 10v. Please help!
Is the current in the collector the same as that in the emitter? Do I need to take into consideration re (little r e, the intrinsic resistance of the resistor)?