SUMMARY
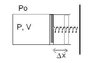
The discussion focuses on calculating the work done by an ideal gas on a Hooke's spring when heat is added, causing both volume and pressure to triple. Key equations include the ideal gas law (Pv = nrT), the work done on the spring (W = (1/2)kx²), and the relationship between pressure and volume during expansion. The final approach involves deriving a linear function for pressure in terms of volume, allowing for the calculation of work without needing to integrate, ultimately simplifying the problem significantly.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of the Ideal Gas Law (Pv = nrT)
- Knowledge of Hooke's Law (F = kx)
- Familiarity with thermodynamic work calculations
- Basic calculus for integration (if needed)
NEXT STEPS
- Study the derivation of work done in thermodynamic processes, focusing on isothermal and adiabatic conditions.
- Learn about the relationship between pressure, volume, and temperature in ideal gases.
- Explore Hooke's Law applications in mechanical systems.
- Investigate the concept of quasi-static processes in thermodynamics.
USEFUL FOR
Students in physics or engineering, particularly those studying thermodynamics, mechanical systems, or preparing for exams involving gas laws and spring mechanics.