haxor489
- 25
- 0
I don't quite have a good understanding of what exactly the neper frequency is. I've seen it derived it from certain circuits before and it was never really clear what it was. In a series RLC circuit it was simple enough to find since we were given a nice second order differential from which to take to the S domain and solve for with a quadratic formula and then pull out the neper frequency from :
-α +-√α2-ωo2
α-neper frequency
ωo- resonant radian frequency
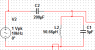
In a filter such as (see attachment) how would one derive the neper frequency since it does not fall so neatly into a second order polynomial. I get
s2-[1/(L1(C1+C2)]
which doesn't fall so neatly into the quadratic formula nor has a term in the first order. Am i to assume this filter has no neper frequency? Or a Q factor?
Thanks for your time
-α +-√α2-ωo2
α-neper frequency
ωo- resonant radian frequency
In a filter such as (see attachment) how would one derive the neper frequency since it does not fall so neatly into a second order polynomial. I get
s2-[1/(L1(C1+C2)]
which doesn't fall so neatly into the quadratic formula nor has a term in the first order. Am i to assume this filter has no neper frequency? Or a Q factor?
Thanks for your time