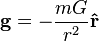Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around the concept of gravitational acceleration in the context of General Relativity (GR) compared to Newtonian mechanics. Participants explore the equations that describe gravitational acceleration in GR and the implications of these equations, particularly near black holes.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory
- Technical explanation
- Debate/contested
- Mathematical reasoning
Main Points Raised
- One participant questions whether the Newtonian equation for gravitational acceleration applies in GR and seeks an equivalent in GR.
- Another participant states that there is no simple equivalent in GR and mentions the gravitation tensor and metric tensor as key components in determining gravitational effects.
- A specific equation for gravitational acceleration in GR is presented, but it is clarified that the variable r does not represent a measurable radius near a black hole.
- There is a discussion about whether the presented formula gives acceleration as measured by local or distant clocks, with a participant asserting it is measured by local clocks of an observer at position r.
- Concerns are raised about the proper distance calculations in the Schwarzschild solution, with references to different definitions of proper distance and their implications for simultaneity.
- Another participant provides integrals for calculating Fermi normal distance for both stationary and free-falling observers, indicating a mathematical approach to the discussion.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express differing views on the interpretation of gravitational acceleration in GR, the meaning of the variable r in the equations, and the definitions of proper distance. No consensus is reached on these points.
Contextual Notes
There are limitations regarding the definitions of terms like "proper distance" and the assumptions underlying the calculations presented. The discussion highlights the complexity of measuring gravitational effects in the context of GR, particularly near black holes.