HumanistEngineer
- 18
- 2
I have a working Matlab code solving the 1D convection-diffusion equation to model sensible stratified storage tank by use of Crank-Nicolson scheme (without εeff in the below equation).
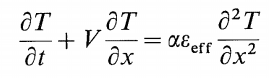
As indicated by Zurigat et al; there is an additional mixing effect having a hyperbolic decaying form from the top of the tank to the bottom (at the inlet we have a high rate of mixing). So I try to involve εeff as a magnifying effect on the thermal diffusivity as shown in the equation above. Please see the section Inlet Mixing in the Matlab code below.
The problem is that: there occurs an abnormal temperature increase more than the coming inlet temperature whenever I involve the mixing effect as a hyperbolic decaying form (please see pictures below).
Would you please tell me why I have this abnormal temperature increase problem? I tried also Forward-Time Central Space method and CN with upwind treatment but at all approaches, I encountered this abnormal issue. Any solution please? I am not so experienced with the finite difference methods!
With εeff involved, the problem with abnormal temperature increase encountered:
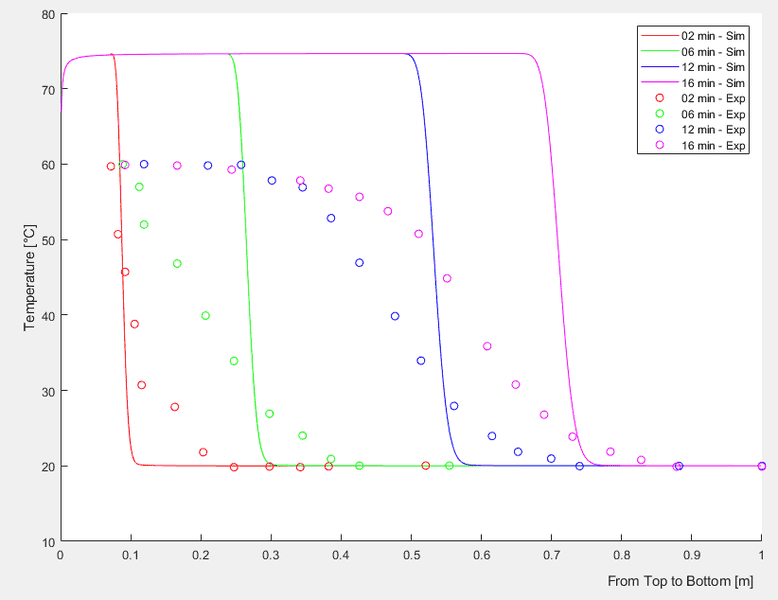
The case without εeff, the solution of convection-diffusion equation for a stratified sensible storage tank by use of Crank-Nicolson scheme:

Matlab Code:
As indicated by Zurigat et al; there is an additional mixing effect having a hyperbolic decaying form from the top of the tank to the bottom (at the inlet we have a high rate of mixing). So I try to involve εeff as a magnifying effect on the thermal diffusivity as shown in the equation above. Please see the section Inlet Mixing in the Matlab code below.
The problem is that: there occurs an abnormal temperature increase more than the coming inlet temperature whenever I involve the mixing effect as a hyperbolic decaying form (please see pictures below).
Would you please tell me why I have this abnormal temperature increase problem? I tried also Forward-Time Central Space method and CN with upwind treatment but at all approaches, I encountered this abnormal issue. Any solution please? I am not so experienced with the finite difference methods!
With εeff involved, the problem with abnormal temperature increase encountered:
The case without εeff, the solution of convection-diffusion equation for a stratified sensible storage tank by use of Crank-Nicolson scheme:
Matlab Code:
Code:
function [T,dh,dt] = CDR_CrankNicolson_Exp_InletMixing(t_final,n)
%% 1D Convection-Diffusion-Reaction (CDR) equation - Crank-Nicolson scheme
% solves a d2u/dx2 + b du/dx + c u = du/dt
%% References
% pg. 28 - http://www.ehu.eus/aitor/irakas/fin/apuntes/pde.pdf
% pg. 03 - https://www.sfu.ca/~rjones/bus864/notes/notes2.pdf
% http://nptel.ac.in/courses/111107063/24
tStart = tic; % Measuring computational time
%% INPUT
% t_final : overall simulation time [s]
% n : Node number [-]
%% Tank Dimensions
h_tank=1; % [m] Tank height
d_tank=0.58; % [m] Tank diameter
vFR=11.75; % [l/min] Volumetric Flow Rate
v=((vFR*0.001)/60)/((pi*d_tank^2)/4); % [m/s] Water velocity
dh=h_tank/n; % [m] mesh size
dt=1; % [s] time step
maxk=round(t_final/dt,0); % Number of time steps
% Constant CDR coefficients | a d2u/dx2 + b du/dx + c u = du/dt
a_const=0.15e-6; % [m2/s]Thermal diffusivity
b=-v; % Water velocity
c=0; %! Coefficient for heat loss calculation
%% Inlet Mixing - Decreasing hyperbolic function through tank height
eps_in=2; % Inlet mixing magnification on diffusion
A_hyp=(eps_in-1)/(1-1/n);
B_hyp=eps_in-A_hyp;
Nsl=1:1:n;
eps_eff=A_hyp./Nsl+B_hyp;
a=a_const.*eps_eff; % Case 0
% a=ones(n,1)*a_const; % Case 1
% a=ones(n,1)*a_const*20; % Case 2
%% Initial condition - Tank water at 20 degC
T=zeros(n,maxk);
T(:,1)=20;
%% Boundary Condition - Inlet temperature at 60 degC
T(1,:)=60;
%% Formation of Tridiagonal Matrices
% Tridiagonal Matrix @Left-hand side
subL(1:n-1)=-(2*dt*a(1:n-1)-dt*dh*b); % Sub diagonal - Coefficient of u_i-1,n+1
maiL(1:n-0)=4*dh^2+4*dt*a-2*dh^2*dt*c; % Main diagonal - Coefficient of u_i,n+1
supL(1:n-1)=-(2*dt*a(1:n-1)+dt*dh*b); % Super diagonal - Coefficient of u_i+1,n+1
tdmL=diag(maiL,0)+diag(subL,-1)+diag(supL,1);
% Tridiagonal Matrix @Right-hand side
subR(1:n-1)=2*dt*a(1:n-1)-dt*dh*b; % Sub diagonal - Coefficient of u_i-1,n
maiR(1:n-0)=4*dh^2-4*dt*a-2*dh^2*dt*c; % Main diagonal - Coefficient of u_i,n
supR(1:n-1)=2*dt*a(1:n-1)+dt*dh*b; % Super diagonal - Coefficient of u_i+1,n
tdmR=diag(maiR,0)+diag(subR,-1)+diag(supR,1);
%% Boundary Condition - Matrices
tdmL(1,1)=1; tdmL(1,2)=0;
tdmL(end,end-1)=0; tdmL(end,end)=1;
tdmR(1,1)=1; tdmR(1,2)=0;
tdmR(end,end-1)=1; tdmR(end,end)=0;
MMtr=tdmL\tdmR;
%% Solution - System of Equations
for j=2:maxk % Time Loop
Tpre=T(:,j-1);
T(:,j)=MMtr*Tpre;
if T(end,j)>=89.9
T(:,j+1:end)=[];
finishedat=j*dt;
ChargingTime=sprintf('Charging time is %f [s]', finishedat)
tElapsed = toc(tStart);
SimulationTime=sprintf('Simulation time is %f [s]',tElapsed)
return
end
end
end