- #1
bibo_dvd
- 37
- 0
Hello Guys !
While Studing coupling transformers i found this problem
i tried to solve it
but i don't know if my solving is right or no !
so tell me :)
The problem :
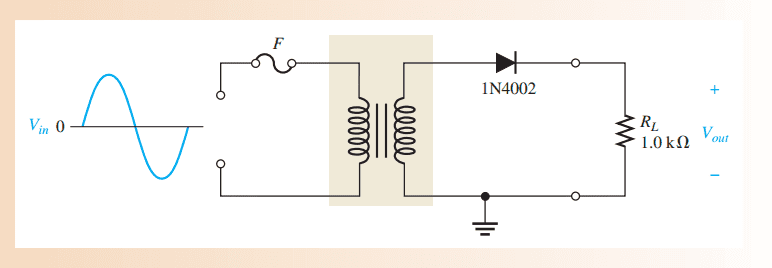

My solve is :
V(out)=nV(in)
V(out)= 2 * 312 = 624 v
PIV = V(out) = 624 v
and if the diode is turned around it will be reversed biased so no current will pass across RL and
Output voltage will equal to zero ..
am i right guys or what ??
Thank you !
While Studing coupling transformers i found this problem
i tried to solve it
but i don't know if my solving is right or no !
so tell me :)
The problem :
My solve is :
V(out)=nV(in)
V(out)= 2 * 312 = 624 v
PIV = V(out) = 624 v
and if the diode is turned around it will be reversed biased so no current will pass across RL and
Output voltage will equal to zero ..
am i right guys or what ??
Thank you !