SUMMARY
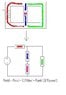
The discussion centers on the addition of reluctances in magnetic circuits, specifically comparing them to electrical circuits. It is established that when reluctances are arranged in a series configuration, they are summed as R(t) = R1 + R2 + ... However, the user questions whether this principle holds true when reluctance is applied to parallel configurations. The consensus is that reluctance behaves similarly to resistance, indicating that the rules for parallel addition do not apply in the same manner for magnetic circuits.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of magnetic circuits and their properties
- Familiarity with the concept of reluctance in magnetism
- Knowledge of series and parallel circuit configurations
- Basic principles of electrical resistance and its relation to reluctance
NEXT STEPS
- Research the mathematical formulation of reluctance in magnetic circuits
- Study the differences between series and parallel configurations in magnetic systems
- Explore practical applications of magnetic circuits in engineering
- Learn about the relationship between reluctance and magnetic flux
USEFUL FOR
Students of electrical engineering, physicists studying magnetism, and professionals designing magnetic circuits will benefit from this discussion.