SUMMARY
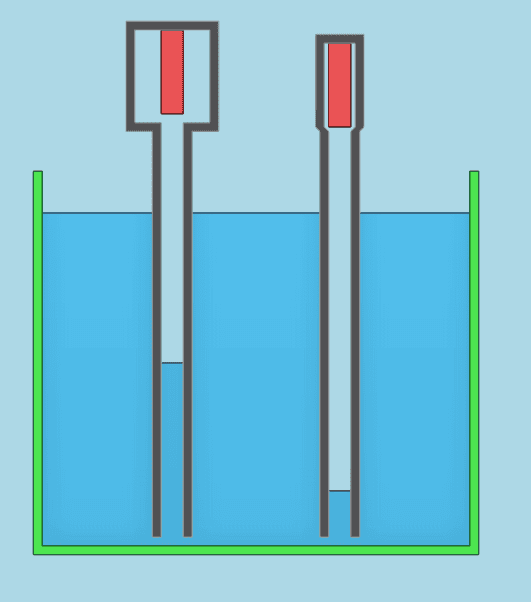
The discussion centers on the behavior of pressure sensors in two closed containers with differing air volumes submerged in water. The pressure sensor in the container with less air volume (right) will read a higher pressure than the sensor in the container with more air volume (left). This occurs because the gas pressure in the right container is able to exert greater force on the water column, pushing it further downwards. The conclusion is that pressure readings will not be identical due to the differences in air volume affecting the pressure exerted on the liquid surface.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of basic fluid mechanics
- Knowledge of pressure measurement techniques
- Familiarity with gas laws, particularly Boyle's Law
- Experience with pressure sensors and their applications
NEXT STEPS
- Research the principles of fluid statics and dynamics
- Learn about Boyle's Law and its implications in closed systems
- Explore the functionality and calibration of pressure sensors
- Investigate the effects of air volume on pressure readings in different scenarios
USEFUL FOR
This discussion is beneficial for students and professionals in physics, engineering, and environmental science, particularly those interested in fluid dynamics and pressure measurement techniques.