DarkerStorm
- 4
- 0
Homework Statement
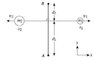
Two particles move in opposite directions along a straight line. Particle 1 of mass m1 = 23 kg at x1 = 16 m moves with a speed v1 = 34 m/s (to the right), while the particle 2 of mass m2 = 64 kg at x2 = −25 m moves with a speed v2 = −43 m/s (to the left). Given: Counter-clockwise is the positive angular direction.
1)What is the total angular momentum of the system about the z-axis relative to point A along y-axis if d1 = 13 m? Answer in units of kgm2/s.
2) What is the total angular momentum of the system about the z-axis relative to point B along y-axis if d2 = 22 m? Answer in units of kgm2/s.
m1 = 23
Position1 = {16 i, 0 j, 0 k}
v1 = {34 i, 0 j, 0 k}
m2 = 64
Pos2 = {-25 i , 0 j, 0 k}
v2 = {-43 i, 0 j, 0 k}
d1 = {0 i, -13 j, 0 k}
d2 = {0 i, 22 j, 0 k}
Homework Equations
L = Position \times m v
The Attempt at a Solution
I got number 1 correct, and number 2 should be the same. however just changing d1 to d2 does not give the correct answer.
1)
{16, 0 , 0} + {0, -13, 0} = {16, -13, 0}
{-25 , 0, 0}+ {0, -13, 0} = {-25, -13, 0}
{16, -13, 0} \times (23 {34 , 0 , 0 }) +
{-25, -13, 0} \times (64 {-43 , 0 , 0 }) = {0, 0, -25610} = 25610 k
2) should be the same but I get {0, 0, 43340} which is incorrect