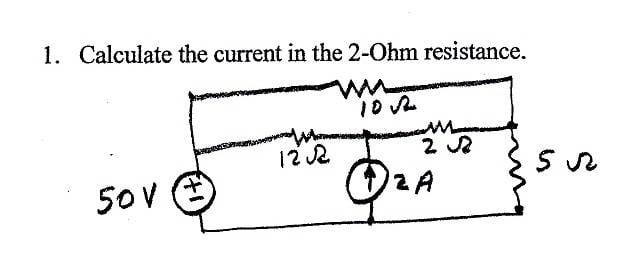
Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around applying Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL) and Thevenin's theorem to solve a circuit problem involving resistors and current sources. Participants explore various methods to analyze the circuit, including superposition and voltage division, while addressing specific challenges in calculating voltages and currents through different components.
Discussion Character
- Homework-related
- Technical explanation
- Exploratory
- Debate/contested
Main Points Raised
- One participant expresses uncertainty about whether to use KCL or Thevenin's theorem first, particularly in relation to the current through a 2 ohm resistor.
- Another suggests using KCL and KVL to set up equations for the unknown currents in the circuit.
- Superposition is proposed as an alternative method to analyze the circuit by considering one source at a time.
- A participant struggles with calculating Thevenin voltage and resistance, indicating confusion about the circuit configuration.
- There is a discussion about the implications of having no current flowing through a branch and its effect on voltage assumptions.
- Participants challenge each other's assumptions about voltage drops across resistors and the potential at various nodes.
- One participant realizes that moving the 10 ohm resistor changes the circuit's configuration and affects current flow.
- There is a debate about the potential at terminal nodes and the validity of assumptions regarding voltage when only a current source is present.
- Some participants note the importance of correctly labeling nodes and understanding their relationships to reference nodes.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants do not reach a consensus on the best approach to solve the circuit problem. Multiple competing views on the application of KCL, Thevenin's theorem, and superposition remain, with ongoing challenges and corrections to assumptions made throughout the discussion.
Contextual Notes
Participants express uncertainty about specific voltage drops and current distributions, indicating potential limitations in their assumptions and calculations. The discussion reflects the complexity of circuit analysis and the need for careful consideration of node potentials and circuit configurations.