- #1
bikertomm
- 1
- 0
Hi all, I'm new to the forum and have a query with one of my most recent assignments.
This one is called 'The flywheel' to do with moments of inertia. I have completed the first lot of calculations using the formula no problem.
My average experimental value came out at 0.49 kg m(2)
And the theory calculation came out at 0.50 kg m(2)
Question 2 & 3 are the ones I'm struggling with:
Question number 2 says to discuss the effect of bearing friction - I am really struggling to find anything on this.
Question 3 asks how the effect of friction can be determined? I'm struggling with this too. Any help would be massively appreciated..
Here are some pictures of the assignment, cheers.
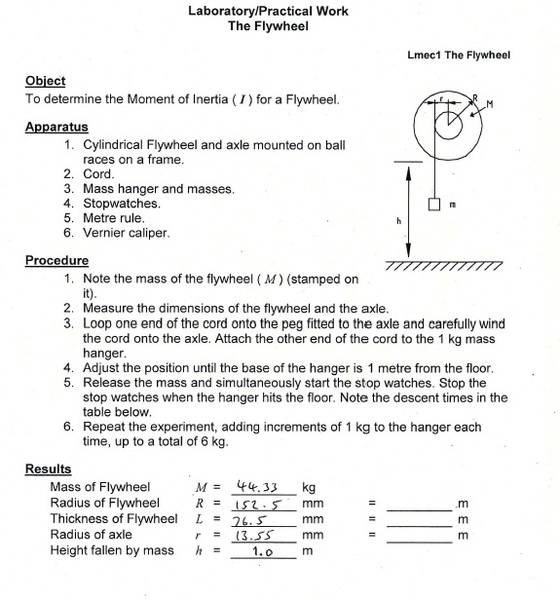


This one is called 'The flywheel' to do with moments of inertia. I have completed the first lot of calculations using the formula no problem.
My average experimental value came out at 0.49 kg m(2)
And the theory calculation came out at 0.50 kg m(2)
Question 2 & 3 are the ones I'm struggling with:
Question number 2 says to discuss the effect of bearing friction - I am really struggling to find anything on this.
Question 3 asks how the effect of friction can be determined? I'm struggling with this too. Any help would be massively appreciated..
Here are some pictures of the assignment, cheers.