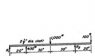
SUMMARY
The discussion centers on calculating the maximum bending stress in a beam with a specified diameter of 2.5 inches. The user has already determined the reactions, R1 at 50 and R2 at 650, but seeks clarification on how the beam's diameter influences the bending moment diagrams and the calculation of maximum stress. The diameter affects the moment of inertia, which is crucial for determining bending stress at the point of maximum moment. Understanding these relationships is essential for accurate stress calculations in structural engineering.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of beam mechanics and bending stress calculations
- Familiarity with moment of inertia and its role in bending stress
- Knowledge of how to draw bending moment diagrams
- Basic principles of static equilibrium in structural analysis
NEXT STEPS
- Study the relationship between diameter and moment of inertia in beam calculations
- Learn how to derive bending stress formulas using the diameter of beams
- Research methods for drawing accurate bending moment diagrams
- Explore advanced topics in structural analysis, such as shear stress and deflection
USEFUL FOR
Structural engineers, civil engineering students, and professionals involved in beam design and analysis will benefit from this discussion.