- #1
lforster02
- 1
- 0
I am trying to calculate the theoretical thickness of an anodised coating. I know all values apart from I am unsure whether to use 2e or 6e for the amount of electrons.
Anode reaction as follows: 2OH = H2O + O + 2e
the aluminium reactions preferentially with the one O atom, using equation: 3O + 2Al (anode) = Al2O3
There is 2 electrons transferred in the anode reaction, although 3O consumed to produce the coating Al2O3, which means 6e is transferred. Does anyone have any idea whether to use 6 or 2 in the formula: thickness = (1/density) x ((molecular mass x current x time) / (area x number of e x faradays constant))
Attached are the relevant reactions
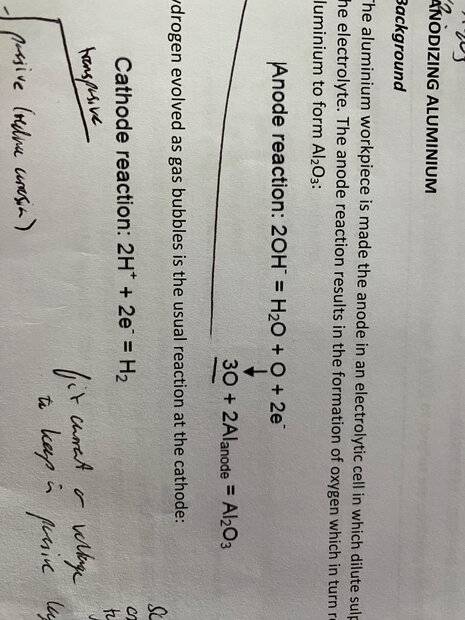
Anode reaction as follows: 2OH = H2O + O + 2e
the aluminium reactions preferentially with the one O atom, using equation: 3O + 2Al (anode) = Al2O3
There is 2 electrons transferred in the anode reaction, although 3O consumed to produce the coating Al2O3, which means 6e is transferred. Does anyone have any idea whether to use 6 or 2 in the formula: thickness = (1/density) x ((molecular mass x current x time) / (area x number of e x faradays constant))
Attached are the relevant reactions
Last edited by a moderator: