- #1
Mr su
- 1
- 0
- TL;DR Summary
- LM 319 high speed comparator.
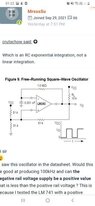
I check the datasheet of LM 319 high speed comparator online. I was wondering if LM 319 can accept negative supply voltage(-10V) and its possible to produce a 10V to -10V square wave which oscillates along origin rather than just 10V to 0v as shown below.