SUMMARY
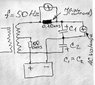
The discussion centers on the behavior of a capacitor connected to a transformer outputting 5V RMS. The final voltage across the capacitor plates is determined by the peak voltage, which is calculated as 2 * SQRT(2) * Vrms. The current through the capacitor is derived using the equation i = C * dV/dt, and it is essential to consider the peak-to-peak voltage amplitude when calculating ripple current. Non-polar capacitors are recommended for handling AC voltages, and their voltage ratings should exceed the RMS value significantly.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of AC voltage waveforms and RMS values
- Familiarity with capacitor types, specifically non-polar capacitors
- Knowledge of the equation i = C * dV/dt for current calculation
- Basic grasp of sine wave equations, particularly V(t) = A sin(ωt)
NEXT STEPS
- Research the characteristics and applications of non-polar capacitors
- Learn how to calculate peak and peak-to-peak voltages from RMS values
- Study the impact of angular frequency (ω) on AC circuits
- Explore ripple current calculations in capacitor circuits
USEFUL FOR
Electrical engineers, electronics students, and hobbyists working with AC circuits and capacitors will benefit from this discussion.