SUMMARY
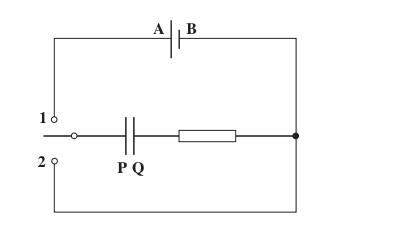
The discussion confirms that when a capacitor charges through a fixed resistor, the potential difference across the resistor decreases exponentially to zero while the potential difference across the capacitor increases exponentially to match the battery voltage. During discharging, the capacitor acts as a power supply, causing both its potential difference and that across the resistor to decrease exponentially. The relationship is governed by Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL), which states that the sum of potential differences in a closed loop must equal zero, leading to the equation VC = -VR.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of capacitor charging and discharging principles
- Familiarity with Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL)
- Knowledge of exponential functions in electrical circuits
- Basic circuit analysis involving resistors and capacitors
NEXT STEPS
- Study the mathematical derivation of capacitor charging and discharging equations
- Learn about RC time constants in circuits
- Explore practical applications of capacitors in timing circuits
- Investigate the effects of different resistor values on charging and discharging rates
USEFUL FOR
Electrical engineering students, circuit designers, and anyone interested in understanding capacitor behavior in electronic circuits.