SUMMARY
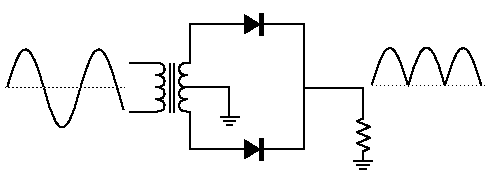
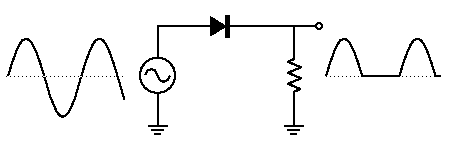
The discussion focuses on the implications of switching the diode orientation in a center-tap rectifier circuit. It is established that reversing the diode will result in a shorted secondary of the transformer during one half of the AC cycle, leading to zero output voltage and potential transformer damage. The participants recommend simulating the circuit using LTspice to visualize the output waveforms and understand the differences between full-wave and half-wave rectification. Additionally, it is noted that a full-wave center-tap rectifier experiences lower voltage and power loss in the diodes compared to a full-wave bridge rectifier.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of center-tap rectifier circuits
- Familiarity with diode operation and characteristics
- Knowledge of AC waveforms and rectification processes
- Experience with LTspice simulation software
NEXT STEPS
- Simulate center-tap rectifier circuits using LTspice
- Explore the differences between full-wave bridge rectifiers and full-wave center-tap rectifiers
- Research synchronous rectification techniques to reduce power loss
- Study the impact of diode orientation on output waveforms in rectifier circuits
USEFUL FOR
Electrical engineers, electronics students, and hobbyists interested in power supply design and rectification techniques.