help I have 12 hours
- 12
- 2
- Homework Statement
- Electromagnetic radiation (known as Cherenkov radiation) is emitted when a charged particle moves through a medium faster then the local speed of light. It should be stressed that the particle is never going faster then the speed of light in vacuum (or c), just faster than the speed of light in the material (which is always less than c).
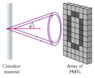
When a charged particle passes straight through a medium faster than the local speed of light, it will emit Cherenkov radiation in a cone. Let's see how the cone angle is correlated to the speed of the particle.
Ring-imaging Cherenkov detectors are devices that can accurately measure the velocity of charged particles as they pass through them. They are very useful as subdetectors in large particle detector systems. Let us look at what decisions need to go into designing a Cherenkov detector.
Suppose our detector used aerogel (n=1.03) for the Cherenkov material and the photomultiplier tube array had a resolution of Δθ=1.2degrees. This means, for instance, that the detector can distinguish between Cherenkov light emitted at an angle of 15 degrees and that emitted at 13.8 degrees but can't tell the difference between Cherenkov light emitted at 15 degrees and that emitted at 13.9 degrees. What is the highest velocity vmax at which a charged particle can be accurately measured to be below the speed of light in vacuum (c
)?
Express your answer as a multiple of c
to three significant figures.
vmax= _________________________(c)
- Relevant Equations
- cos(theta)=c/vn
where theta is the angle at which the cherenkov radiation is emitted.
n is index of refraction
v is velocity of the particle
c speed of light
cos(theta)=c/vn
cos(1.2 degrees)=((3*10^8)/v(1.03))
v=291262135.9
v/c=.971
so the particle is moving at (.971)c
But mastering physics tells me this is wrong, and says that I'm not account for the angle.
I am really stumped.
cos(1.2 degrees)=((3*10^8)/v(1.03))
v=291262135.9
v/c=.971
so the particle is moving at (.971)c
But mastering physics tells me this is wrong, and says that I'm not account for the angle.
I am really stumped.