- #1
moriheru
- 273
- 17
α
 1. Homework Statement
1. Homework Statement
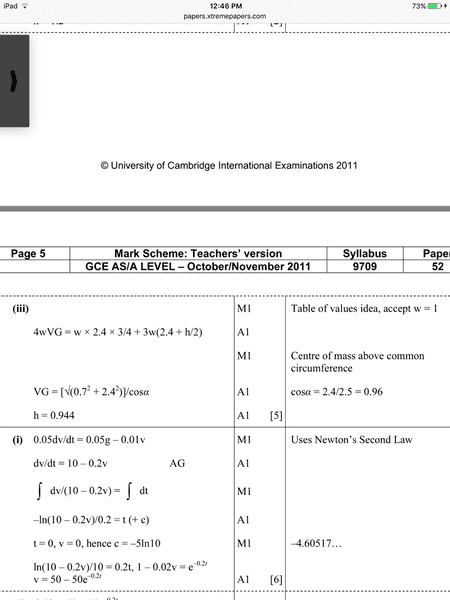
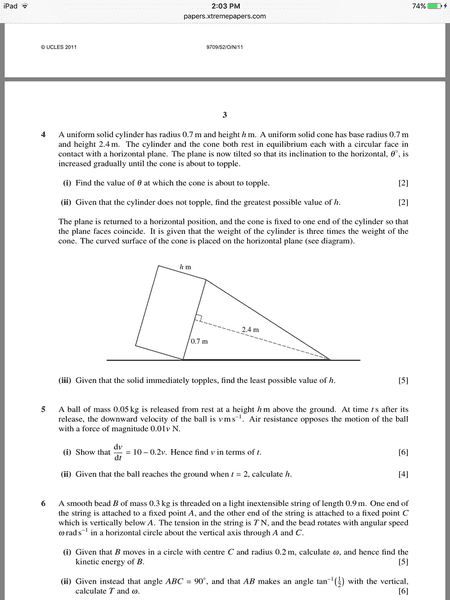
The problem my question is about is 4. (iii). Second image First image is markscheme
The CIE markscheme has h= 0.944 as the least possible value for h. They find this value for h by setting up an equation for the centre of mass of the complete objects and then stating that the centre of mass of the hole object is above the common circumference ( on the side of the cylinder). This all seems clear to me, except for the second equation where the cos() is involved. If anyone could explain that, I would be very grateful .Yet when I first tried the problem myself I attempted to find the value for h by deducing that the moment of the weight of the cylinder about the centre of the common circumference of the complete object must be greater than the moment of the cone about the same point and I found my h to be equal to 0.4. Here is my moments equation:
Let W be the weight of the cone.
3Wx(h/2) = W x ( 2.4x0.25)
Solving for h gives :
h=0.4
If anybody could tell me where I went wrong I would be again very grateful. Finally if anybody wants to check with the markscheme for that exam( the first part labeled with iii above the second image)
Thank you
The problem my question is about is 4. (iii). Second image First image is markscheme
Homework Equations
The Attempt at a Solution
The CIE markscheme has h= 0.944 as the least possible value for h. They find this value for h by setting up an equation for the centre of mass of the complete objects and then stating that the centre of mass of the hole object is above the common circumference ( on the side of the cylinder). This all seems clear to me, except for the second equation where the cos() is involved. If anyone could explain that, I would be very grateful .Yet when I first tried the problem myself I attempted to find the value for h by deducing that the moment of the weight of the cylinder about the centre of the common circumference of the complete object must be greater than the moment of the cone about the same point and I found my h to be equal to 0.4. Here is my moments equation:
Let W be the weight of the cone.
3Wx(h/2) = W x ( 2.4x0.25)
Solving for h gives :
h=0.4
If anybody could tell me where I went wrong I would be again very grateful. Finally if anybody wants to check with the markscheme for that exam( the first part labeled with iii above the second image)
Thank you