- 2,180
- 2,690
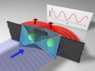
An intense beam of high-energy X-ray photons (violet) hits two adjacent iridium atoms (green) in the crystal. This excites electrons in the atoms for a short time. The atoms emit X-ray photons which overlap behind the two iridium atoms (red) and can be analyzed as interference images.
Credit: Markus Grueninger, University of Cologne
An international research team led by physicists from Collaborative Research Centre 1238, 'Control and Dynamics of Quantum Materials' at the University of Cologne has implemented a new variant of the basic double-slit experiment using resonant inelastic X-ray scattering at the European Synchrotron ESRF in Grenoble. This new variant offers a deeper understanding of the electronic structure of solids. Writing in Science Advances, the research group have now presented their results under the title 'Resonant inelastic x-ray incarnation of Young's double-slit experiment'.
Related news.
Journal reference:
A. Revelli, et al. Resonant inelastic x-ray incarnation of Young’s double-slit experiment. Science Advances, 2019 DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aav4020
Last Edit: Inserted correct picture.
Attachments
Last edited: