SUMMARY
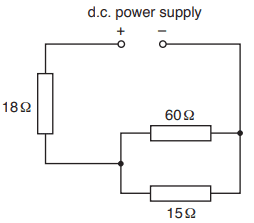
The discussion centers on current division in an electrical circuit containing a 7.5V DC power supply and three resistors: 18 ohms, 15 ohms, and 60 ohms. The largest current flows through the 18 ohm resistor due to its position in the circuit, as all current from the power supply must pass through it before branching to the other resistors. The 60 ohm resistor experiences the smallest current because it has the highest resistance, confirming that current divides inversely with resistance in parallel circuits.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of Ohm's Law
- Knowledge of series and parallel resistor configurations
- Familiarity with electrical circuit terminology
- Basic principles of voltage and current flow
NEXT STEPS
- Study the concept of current division in parallel circuits
- Learn about calculating total resistance in series and parallel circuits
- Explore the application of Ohm's Law in circuit analysis
- Investigate the effects of resistor values on current flow
USEFUL FOR
Electrical engineering students, hobbyists building circuits, and anyone interested in understanding current flow and resistance in electrical systems.