- #1
niaz
- 3
- 0
Hello all,
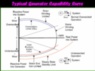
I want to know about turbo alternator real power producing capability under loss of excitation condition.
Normally in salient pole rotor have capability to supply real power under field current=0 condition, as there is reluctance power developed. But what about non salient pole generator? there is no saliency. So, there is not possibility to develop reluctance power. Does it mean that, this type of turbo generator is totally prohibited to run under loss of excitation condition?
I want to know about turbo alternator real power producing capability under loss of excitation condition.
Normally in salient pole rotor have capability to supply real power under field current=0 condition, as there is reluctance power developed. But what about non salient pole generator? there is no saliency. So, there is not possibility to develop reluctance power. Does it mean that, this type of turbo generator is totally prohibited to run under loss of excitation condition?