Discussion Overview
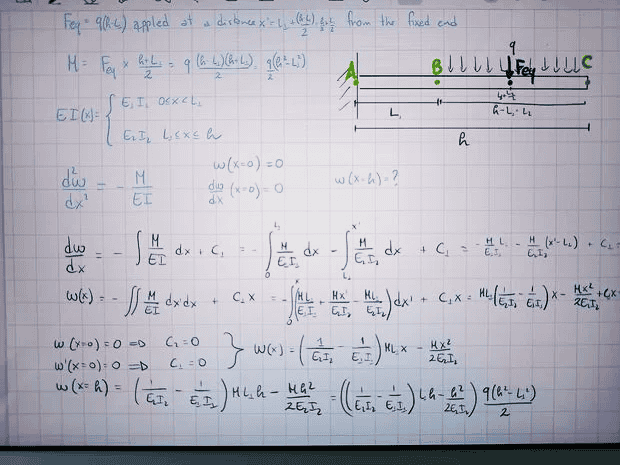
The discussion centers on the deflection of a cantilever beam with a fixed end, subjected to a uniform load applied from a distance L from the fixed end to the free end. The beam has a known rectangular cross-section and a total length h, with varying values of the modulus of elasticity (E) and moment of inertia (I) in two segments of the beam. Participants are exploring the mathematical approach to determine the deflection at the free end, w(h).
Discussion Character
- Technical explanation
- Mathematical reasoning
- Debate/contested
Main Points Raised
- One participant outlines their approach to solving for the deflection w(h) of the beam, indicating the need to consider the different values of E and I in the two segments of the beam.
- Another participant suggests a method for solving the differential equations governing the deflection in each segment, emphasizing the need to apply boundary conditions at the transition point.
- A follow-up question is raised regarding the calculation of the internal moments M1 and M2 for the two segments of the beam.
- Further clarification is sought on how to find the reactions at the fixed end, which are necessary for determining the internal moments.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants are engaged in a technical discussion with no clear consensus yet on the best method for calculating the moments or the deflection. Multiple approaches are being considered, and questions remain about the specifics of the calculations.
Contextual Notes
Participants have not yet resolved the assumptions regarding the loading conditions and the specific methods for calculating the internal moments. The discussion also reflects a dependence on the definitions of the variables used in the equations.