- #1
Eng67
- 21
- 0
I am trying to compute the DTFT of x[n]=n(.5)^n u[n].
This is my work so far.
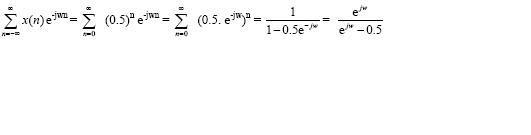
Is this correct?
This is my work so far.
Is this correct?
Discrete-time Fourier Analysis is a mathematical tool used to analyze and represent signals that are sampled at discrete points in time. It allows for the decomposition of a discrete-time signal into its constituent frequencies, similar to how the continuous Fourier transform decomposes continuous signals.
The main difference between discrete-time Fourier Analysis and continuous Fourier Analysis is that the former deals with signals that are sampled at discrete points in time, while the latter deals with continuous signals. This means that discrete-time Fourier Analysis uses a discrete set of frequencies, while continuous Fourier Analysis uses a continuous range of frequencies.
Discrete-time Fourier Analysis has many applications in various fields, such as signal processing, communications, and control systems. It is used to analyze and design filters, determine the frequency content of signals, and perform spectral analysis on sampled data.
The Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) is a mathematical tool that is used to compute the discrete-time Fourier transform of a finite-length signal. It is a discrete version of the continuous Fourier transform and is commonly used in conjunction with discrete-time Fourier Analysis to analyze and process signals.
The Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) is an algorithm used to efficiently compute the Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT). The FFT reduces the number of computations needed to compute the DFT, making it a commonly used method for computing the DFT in practice.