srinaath
- 51
- 2
i am planning to do a small diy wireless power transfer device.
The circuit of the transmitter is
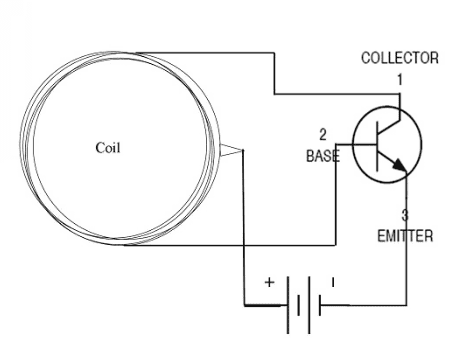
receiver has just the coil and load arrangement.
my query is, (please correct me if am wrong)
-->to induce a voltage in the secondary coil, there must be a varying magnetic field right?
-->but according to circuit, the transistor doesn't help in changing the polarity, what is the necessity of using the transistor then?
am just a hobbyist.
thanks much for your reply in advance.
The circuit of the transmitter is
receiver has just the coil and load arrangement.
my query is, (please correct me if am wrong)
-->to induce a voltage in the secondary coil, there must be a varying magnetic field right?
-->but according to circuit, the transistor doesn't help in changing the polarity, what is the necessity of using the transistor then?
am just a hobbyist.
thanks much for your reply in advance.