okaythanksbud
- 10
- 0
- TL;DR
- The torque on a spinning charge seems like it would change the magnetic moment to be more aligned with the B field but is this actually the case?
If we have a spinning spherical charge in a nonuniform magnet field that points in one direction (for simplicity lets say B=<0,0,k*z>). Since the magnetic field is nonuniform, there will be a force exerted on the dipole, F=(mu•∇)B=mu_z*k. So in this case we expect it to be constant. This is dependent on the assumption that mu•B stays constant
However, we are neglecting torque. Upon first glance wed expect the torque to push the charge to align the dipole moment with the magnetic field. However, the torque points perpendicular to the magnetic field and the dipole moment, so it seems like the angular momentum in the direction of the B field (and hence the magnetic moment) would stay constant, while the angular momentum perpendicular to mu and B would change. So just like this image indicates, I'd expect the motion due to torque to not affect mu_z, which would keep F=(mu•∇)B constant.
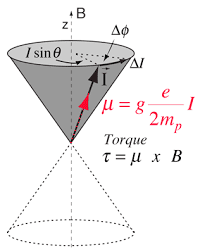
Even though its the unintuitive answer, I'm lead to believe that mu*B, and hence the force of the dipole in the B field would stay constant. Am I correct in this?
However, we are neglecting torque. Upon first glance wed expect the torque to push the charge to align the dipole moment with the magnetic field. However, the torque points perpendicular to the magnetic field and the dipole moment, so it seems like the angular momentum in the direction of the B field (and hence the magnetic moment) would stay constant, while the angular momentum perpendicular to mu and B would change. So just like this image indicates, I'd expect the motion due to torque to not affect mu_z, which would keep F=(mu•∇)B constant.
Even though its the unintuitive answer, I'm lead to believe that mu*B, and hence the force of the dipole in the B field would stay constant. Am I correct in this?